

People who have arthritis or a swollen joint because of an injury might want to try heat. Heat, especially moist heat, can help with joint effusion and joint pain.At-home remedies for joint effusion include: If your joint swells from fluid, there are a few steps you can take yourself. What can I do at home to treat joint effusion? They can help you figure out the best treatment for your joint effusion. Some steroids get swallowed, and others are injected right into your knee joint.Ĭontact your healthcare provider when you need treatment for a swollen joint. Arthritis can cause inflammation, and inflammation can cause joint effusion. Steroids help block inflammatory chemicals.

It helps with pain, inflammation and joint effusion.
#Fluid in knee full#
Pus is a protein-rich liquid that’s full of dead white blood cells. When you have an infection, your joint tissues can fill with pus. You might need a joint replacement - a type of surgery - because of it. Septic arthritis is a serious disease that can damage or even destroy your joint. An infection in your joint is called septic arthritis. There are several reasons why your knee or other joints might swell with fluid. What are the most common causes of joint effusion (swollen joint)? These are symptoms of various diseases and conditions. Other symptoms that often go along with a swollen joint include: The fluid can consist of several substances, including:īut, if there are more fluids than usual in your joint, you have effusion (a swollen knee joint). Ordinarily, there is a little bit of fluid already in the joint tissues.
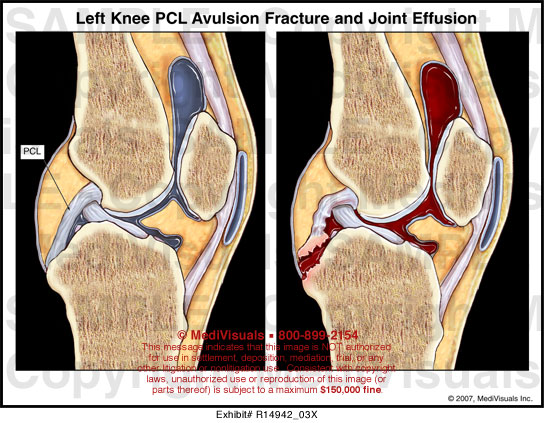
Joint effusion can also affect your small joints, such as your: Joint effusion can affect your knee and other big joints. Joint effusion is when fluids enter one or more of these tissues. They control how your joints move.Īll of these bones and tissues work together to help your joints function - to help them bend, flex, straighten, rotate and bear your weight. This important tissue lubricates your joints with a sticky liquid called synovial fluid. The elastic band-like ligaments connect your bones and support your joints. This slick tissue protects your knee by keeping your bones from rubbing directly together. Cartilage covers each bone where it connects at your joints. These sacks of fluid act like protective cushions between your bones, ligaments and other parts of your joints. Your knee, for example, is made up of three bones:īut your joints also consist of tissues that have various purposes: Your bones form joints when two or more of them connect. The fluids make your joint look larger and puffier compared to your other joints. Joint effusion (a swollen joint) happens when extra fluids flood the tissues around your joint. A swollen synovial bursa inside a knee joint What is joint effusion?


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
